2D Maxwell equations using Nedelec elements#
XLiFE++ provides Nedelec elements (first and second family) that are H(curl) conforming. Consider the following academic Maxwell problem:
The variational formulation in \(V=\left\{\mathbf{v}\in H(curl,\Omega),\ \mathbf{v}\times n=0 \mathrm{\;on\;}\partial \Omega\right\}\) is to find:
Using first family Nedelec’s element, the XLiFE++ program looks like:
#include "xlife++.h"
using namespace xlifepp;
Real omg=1, eps=1, mu=1, a=pi_, ome=omg* omg* mu* eps;
Vector<Real> f(const Point& P, Parameters& pa = defaultParameters)
{
Real x=P(1), y=P(2);
Vector<Real> res(2);
Real c=2*a*a-ome;
res(1)=-c*cos(a*x)*sin(a*y);
res(2)= c*sin(a*x)*cos(a*y);
return res;
}
Vector<Real> solex(const Point& P, Parameters& pa = defaultParameters)
{
Real x=P(1), y=P(2);
Vector<Real> res(2);
res(1)=-cos(a*x)*sin(a*y);
res(2)= sin(a*x)*cos(a*y);
return res;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
init(argc, argv, _lang=en);
// mesh square using gmsh
SquareGeo sq(_xmin=0, _xmax=1, _ymin=0, _ymax=1, _nnodes=50, _side_names="Gamma");
Mesh mesh2d(sq, _shape=triangle, _generator=gmsh);
Domain omega=mesh2d.domain("Omega");
Domain gamma=mesh2d.domain("Gamma");
// define space and unknown
Space V(_domain=omega, _FE_type=Nedelec, _order=1, _name="V");
Unknown e(V, _name="E");
TestFunction q(e, _name="q");
// define forms, matrices and vectors
BilinearForm aev=intg(omega, curl(e)|curl(q)) - ome*intg(omega, e|q);
LinearForm l=intg(omega, f|q);
EssentialConditions ecs = (ncross(e)|gamma=0);
// compute
TermMatrix A(aev, ecs, _name="A");
TermVector b(l, _name="B");
// solve
TermVector E=directSolve(A, b);
// P1 interpolation, L2 projection on H1
Space W(_domain=omega, _interpolation=P1, _name="W");
TermVector EP1=projection(E, W, 2);
saveToFile("E.vtu", EP1, _data_name="E");
return 0;
}
As Nedelec finite elements approximation are not conforming in \(H^1(\Omega)\), the solution is not continuous across elements (only tangent component is continuous). So to represent the solution, it is projected on \(H^1(\Omega)\) as follows, by finding:
Using an H1 conforming approximation for \(\mathbf{E}_1\) leads to a continuous representation of the projection. We show on the next figure the \(E_x\) component field provided by this example:
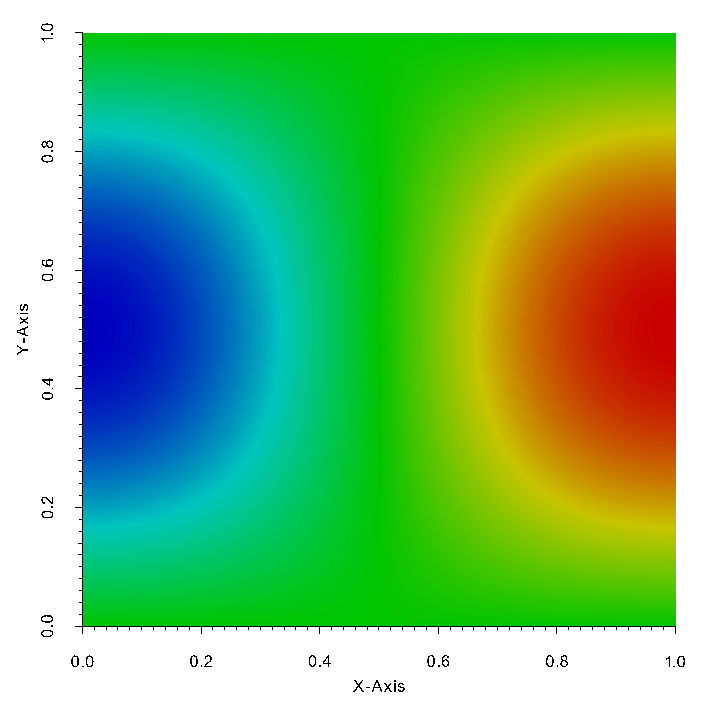
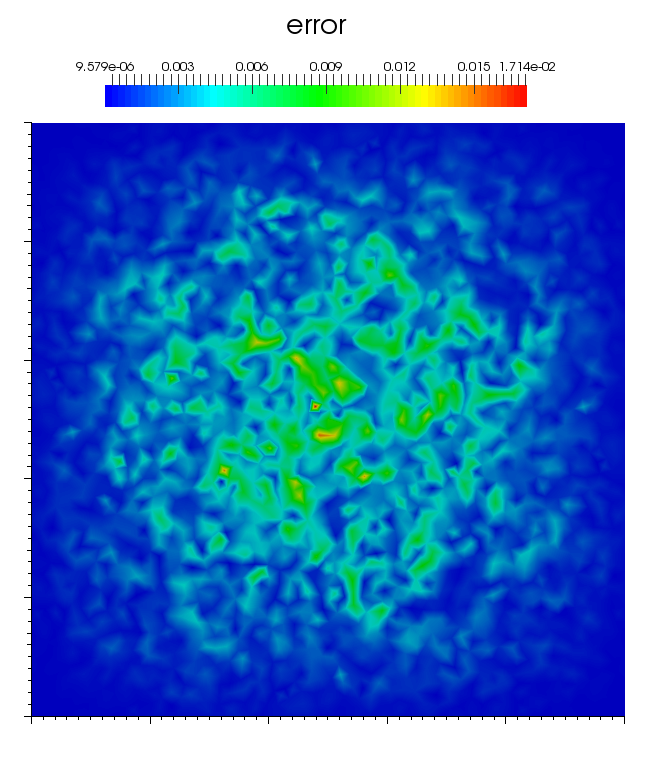
Fig. 7 First component of the solution of the Maxwell 2D problem using Nedelec first family elements, and nodal error#
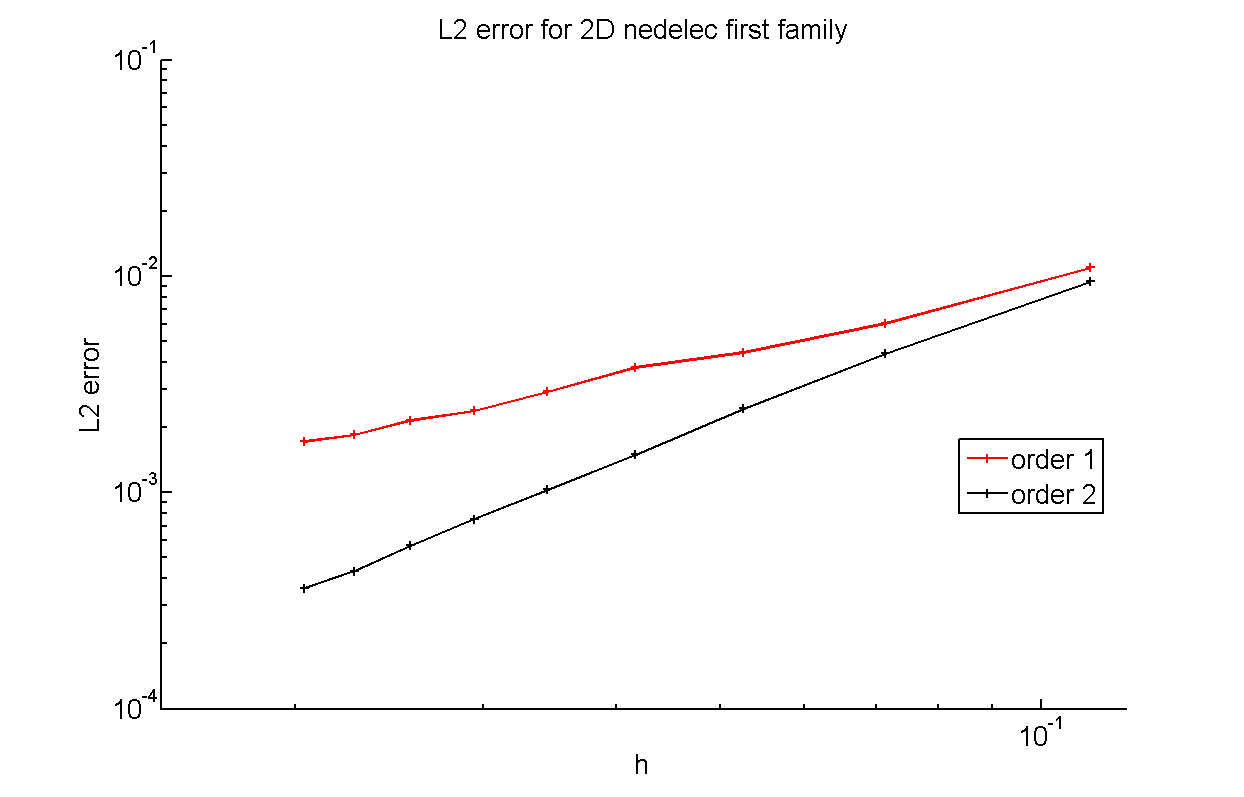
Fig. 8 \(L^2\) errors versus the step \(h\) for 1 and 2 order Nedelec first family approximation#
