2D Laplace problem with transmission condition#
We turn to the Laplace problem with transmission condition:
\[\begin{split}\begin{cases}
-\Delta u^- = f & \mathrm{\;in\;}\Omega^- \\
-\Delta u^+ = f & \mathrm{\;in\;}\Omega^+ \\
u_{|\Sigma^-}=1 \mathrm{\;and\;} u_{|\Sigma^+}=1 & \\
u^-_{|\Gamma}=u^+_{|\Gamma} \mathrm{\;and\;} \partial_x u^-_{|\Gamma}=\partial_x u^+_{|\Gamma} &
\end{cases}\end{split}\]
Its variational formulation in
\[V=\{(v^-,v^+) \in H^1(\Omega^-)\times H^1(\Omega^+),\ v^-_{|\Sigma^-}=0, v^+_{|\Sigma^-}=0,\
v^-_{|\Gamma}=v^+_{|\Gamma}\}\]
is
\[\begin{split}\left|\begin{array}{c}
\mathrm{find\;}(u^-,u^+)\in H^1(\Omega^-)\times H^1(\Omega^+),u^-_{|\Sigma^-}=1, u^+_{|\Sigma^-}=1,\
u^-_{|\Gamma}=u^+_{|\Gamma} \mathrm{\;such\;that\;} \\
\displaystyle \int_{\Omega^-} \nabla u^-.\nabla v^- + \int_{\Omega^+} \nabla u^+.\nabla v^+ =\int_{\Omega^-} f\,v^- + \int_{\Omega^+} f\,v^+ \quad \forall v\in V.
\end{array}
\right.\end{split}\]
Note that derivatives matching is taken into account in a weak sense. The implementation in XLiFE++, using \(P^2\) Lagrange finite element, looks like:\
#include "xlife++.h"
using namespace xlifepp;
Real f(const Point& P, Parameters& pa = defaultParameters)
{
return -8.;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
init(argc, argv, _lang=en); // mandatory initialization of xlifepp
// mesh domain
Strings sn(4);
sn[1] = "x=1/2-"; sn[3] = "x=0";
Rectangle r1(_xmin=0, _xmax=0.5, _ymin=0, _ymax=1, _nnodes=Numbers(20, 40), _domain_name="Omega-", _side_names=sn);
Mesh mesh2d(r1, triangle, 1, _structured);
sn[1] = "x=1"; sn[3] = "x=1/2+";
Rectangle r2(_xmin=0.5, _xmax=1, _ymin=0, _ymax=1, _nnodes=Numbers(20, 40), _domain_name="Omega+", _side_names=sn);
Mesh mesh2d_p(r2, _shape=triangle, _generator=structured);
mesh2d.merge(mesh2d_p);
Domain omegaM=mesh2d.domain("Omega-"), omegaP=mesh2d.domain("Omega+");
Domain sigmaM=mesh2d.domain("x=0"), sigmaP=mesh2d.domain("x=1");
Domain gamma=mesh2d.domain("x=1/2- or x=1/2+");
// create P2 interpolation
Space VM(_domain=omegaM, _interpolation=P2, _name="VM");
Unknown uM(VM, _name="u-");
TestFunction vM(uM, _name="v-");
Space VP(_domain=omegaP, _interpolation=P2, _name="VP");
Unknown uP(VP, _name="u+");
TestFunction vP(uP, _name="v+");
// create bilinear form and linear form
BilinearForm auv=intg(omegaM, grad(uM)|grad(vM))+intg(omegaP, grad(uP)|grad(vP));
LinearForm fv=intg(omegaM, f*vM)+intg(omegaP, f*vP);
EssentialConditions ecs= (uM|sigmaM = 1) & (uP|sigmaP = 1) & ((uM|gamma) - (uP|gamma) = 0);
TermMatrix A(auv, ecs, _name="A");
TermVector B(fv, _name="B");
// solve linear system AX=B using LU factorization
TermVector U=directSolve(A, B);
saveToFile("U_LT.vtu", U);
return 0;
}
Here, a tool merging mesh is used to create a two domains mesh. gmsh should be used also. The picture below shows that the solution is continuous across the boundary \(\Gamma\).
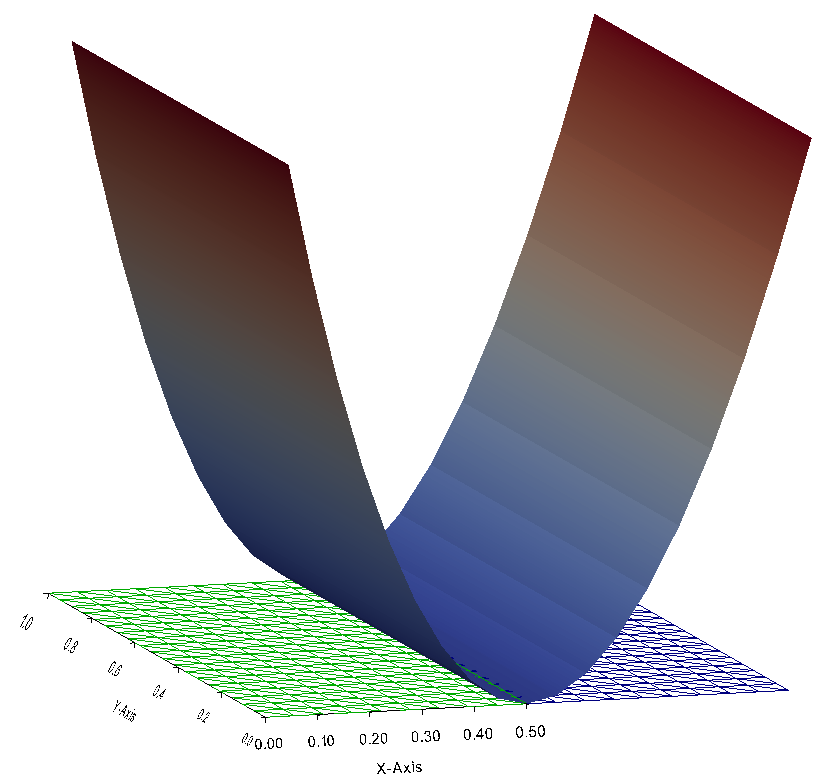
Fig. 17 Solution of the Laplace 2D problem with transmission condition on the unit square \([0,1]^2\)#
