2D Laplace problem with average condition#
As a last example of essential condition, we consider average condition, for instance:
\[\int_\Sigma u=0.\]
Such condition is tricky to take into account in FE softwares. Generally, they do not! Because XLiFE++ uses a powerful process to deal with essential conditions, such condition can be easily addressed:
#include "xlife++.h"
using namespace xlifepp;
Real f(const Point& P, Parameters& pa = defaultParameters)
{return -8.;}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
init(argc, argv, _lang=en); // mandatory initialization of xlifepp
// create a mesh and Domains
SquareGeo sq(_origin=Point(0., 0.), _length=1, _nnodes=10, _domain_name="Omega", _side_names=Strings("y=0", "x=1", "y=1", "x=0"));
Mesh mesh2d(sq, _shape=triangle, _generator=structured);
Domain omega=mesh2d.domain("Omega");
Domain sigmaM=mesh2d.domain("x=0"), sigmaP=mesh2d.domain("x=1");
// create interpolation
Space V(_domain=omega, _interpolation=P2, _name"V");
Unknown u(V, _name="u");
TestFunction v(u, _name="v");
// create bilinear form and linear form
BilinearForm auv=intg(omega, grad(u)|grad(v));
LinearForm fv=intg(omega, f*v);
EssentialConditions ecs= (intg(sigmaM, u) = 0);
TermMatrix A(auv, ecs, _name="A");
TermVector F(fv, _name="B");
// solve linear system AX=F using LU factorization
TermVector U=directSolve(A, F);
saveToFile("U_LA", U, _format=vtu);
return 0;
}
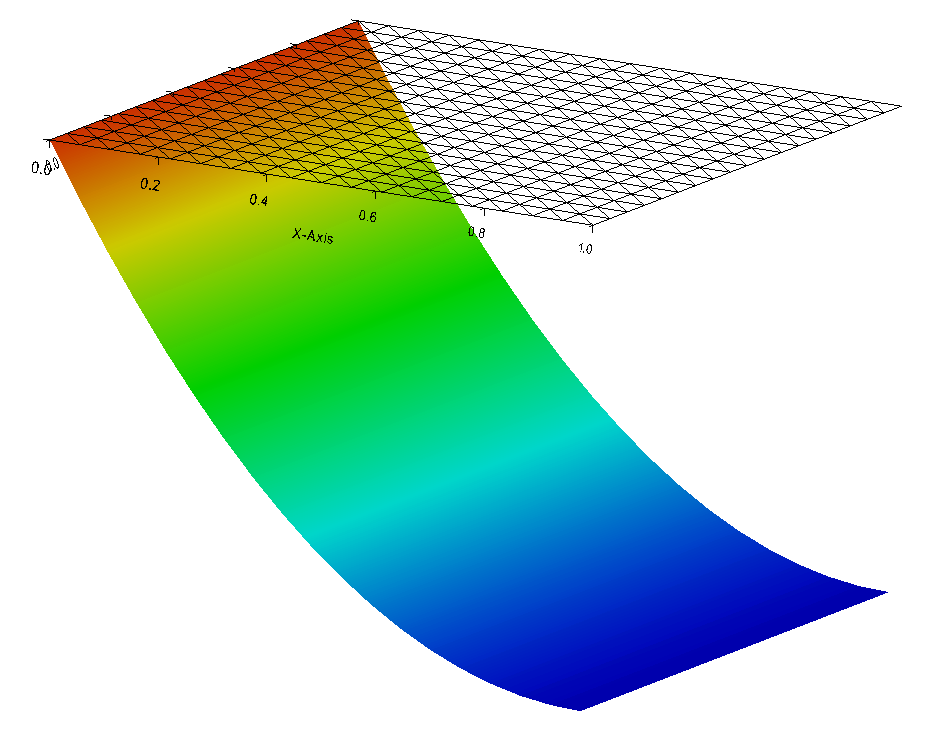
Fig. 2 Solution of the Laplace 2D problem with average condition on the unit square \([0,1]^2\)#
Warning
Beware of some average conditions. For instance, when adding the “full” average condition \(\int_{\Omega} u=0\) the resulting reduced matrix is a full matrix. So, the problem is bigger and slower to solve!
