Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of Laplace operator#
This example shows how to get eigen functions of Laplace operator equipped with homogeneous Neumann condition:
\[\begin{split}\begin{cases}
-\Delta u + u= \lambda u & \mathrm{\;in\;}\Omega \\
\partial_nu=0 & \mathrm{\;on\;} \partial \Omega
\end{cases}\end{split}\]
and its variational formulation in \(V=H^1(\Omega)\):
\[\begin{split}\left|\begin{array}{c}
\mathrm{find\;}(u,\lambda)\in V\times \mathbb{R} \mathrm{\;such\;that\;} \\
\displaystyle \int_\Omega \nabla u.\nabla v + \int_\Omega u\, v =\lambda \int_\Omega u\,v \quad \forall v\in V.
\end{array}
\right.\end{split}\]
#include "xlife++.h"
using namespace xlifepp;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
init(argc, argv, _lang=en); // mandatory initialization of xlifepp
// mesh square
SquareGeo sq(_origin=Point(0., 0.), _length=1, _nnodes=20);
Mesh mesh2d(sq, _shape=triangle, _generator=gmsh);
Domain omega = mesh2d.domain("Omega");
// build P2 interpolation
Space Vk(_domain=omega, _interpolation=P2, _name="Vk");
Unknown u(Vk, _name="u");
TestFunction v(u, _name="v");
// build eigen system
BilinearForm auv = intg(omega, grad(u) | grad(v)) + intg(omega, u * v) ,
muv = intg(omega, u * v);
TermMatrix A(auv, _name="auv"), M(muv, _name="muv");
// compute the 10 first smallest in magnitude
EigenElements eigs = eigenInternSolve(A, M, _nev=10, _mode=krylovSchur, _which="SM"); // internal solver
theCout << eigs.values;
saveToFile("eigs", eigs.vectors, _format=vtu);
return 0;
}
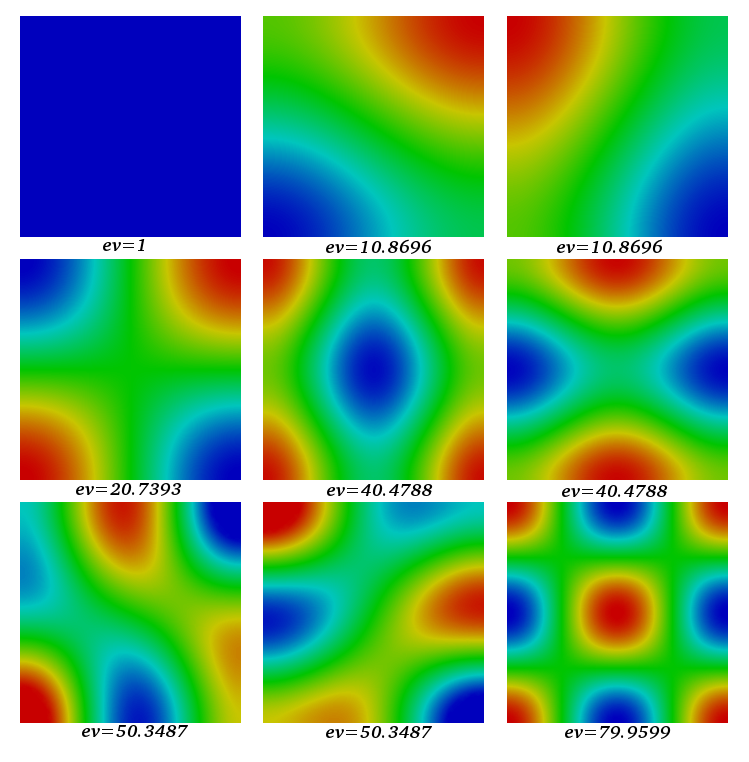
Fig. 25 9 first eigen vectors of the Laplace 2D problem with P2 elements#
