Mixed formulation using P0 and Raviart-Thomas elements#
Consider the Laplace problem with homogeneous Dirichlet condition:
Introducing \(p=\nabla u\), it is rewritten as a mixed problem in \((u,p)\):
The variational formulation in \(V=L^2(\Omega) \times H(div,\Omega)\) is to find:
Note that the Dirichlet boundary condition is a natural condition in this formulation.
The XLiFE++ implementation of this problem using P0 approximation for \(L^2(\Omega)\) and an approximation of \(H(div,\Omega)\) using Raviart-Thomas elements of order 1 is the following:
#include "xlife++.h"
using namespace xlifepp;
Real f(const Point& P, Parameters& pa = defaultParameters)
{ Real x=P(1), y=P(2);
return 32*(x*(1-x)+y*(1-y));}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
init(argc, argv, _lang=en);
// mesh square
SquareGeo sq(_origin=Point(0., 0.), _length=1, _nnodes=21);
Mesh mesh2d(sq, _shape=triangle, _generator=structured);
Domain omega=mesh2d.domain("Omega");
// create approximation P0 and RT1
Space H(_domain=omega, _interpolation=P0, _name="H", _notOptimizeNumbering);
Space V(_domain=omega, _FE_type=RaviartThomas, _order=1, _name="V");
Unknown p(V, _name="p");
TestFunction q(p, _name="q"); // p=grad(u)
Unknown u(H, _name="u");
TestFunction v(u, _name="v");
// create problem (Poisson problem)
TermMatrix A(intg(omega, p|q) + intg(omega, u*div(q)) - intg(omega, div(p)*v));
TermVector b(intg(omega, f*v));
// solve and save solution
TermVector X=directSolve(A, b);
saveToFile("u", X(u), _format=vtu);
return 0;
}
Using Paraview with the Cell data to point data filter that moves P0 data to P1 data and the Warp by scalar filter that produces elevation, the approximated field \(u\) looks like:
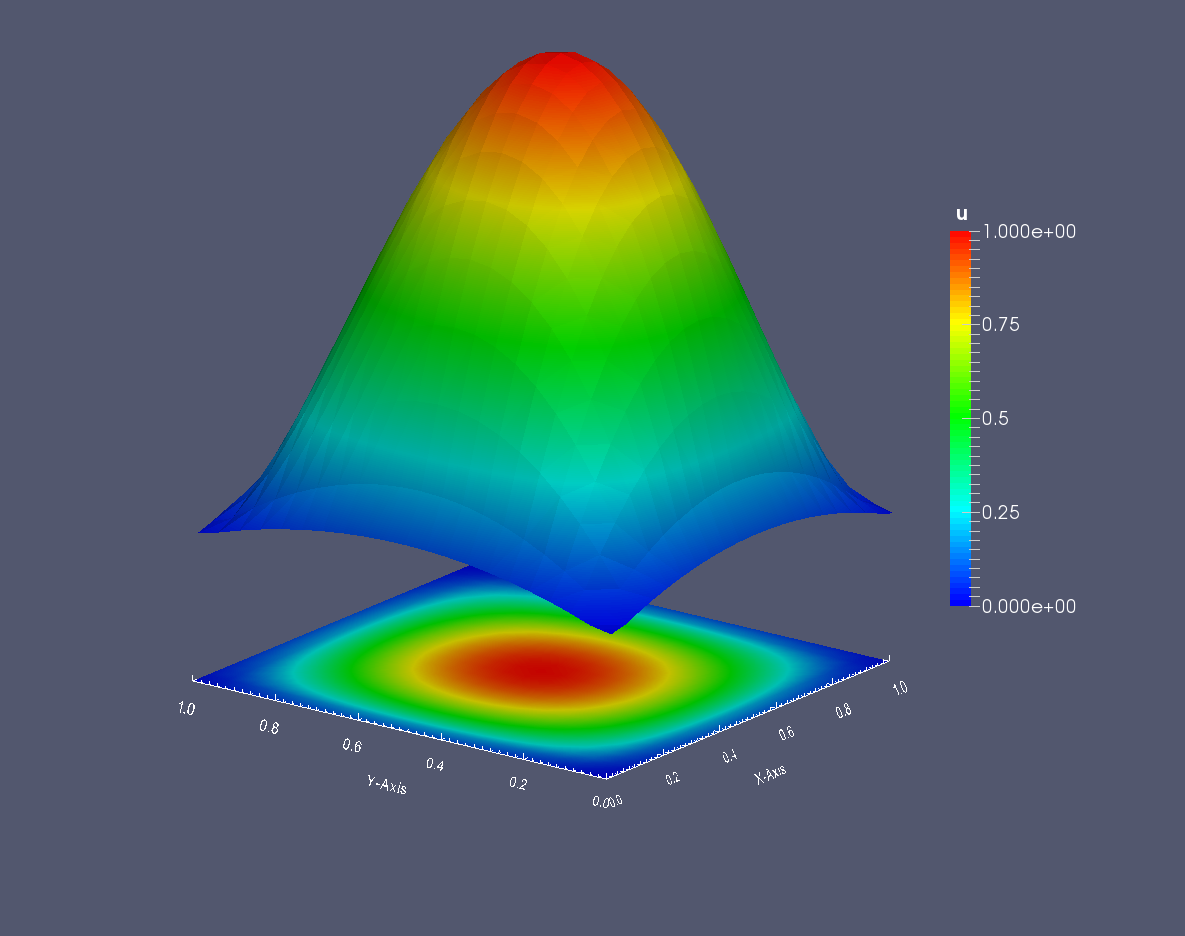
Fig. 5 Solution of the Laplace 2D problem with mixed formulation P0-RT1 on the unit square \([0,1]^2\)#
